by Dr. Yaniv Rotem – Solanaceae Pathologist, Hazera
General background
The Tomato Brown Rugose Fruit Virus – ToBRFV – is a relatively new viral disease, first appearing in the Middle East in 2014. The disease has since spread rapidly to many other areas in the world, and currently constitutes a major global problem in tomato crop production worldwide.
In Israel, all tomato production areas have been severely affected by ToBRFV, and the effects of the disease are evident both in the tomato greenhouses and fields, and in the quality and appearance of the fruits which are sold.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, the symptoms of the disease are similar to the typical symptoms of ToMV, but the severity of the symptoms can differ from that known with ToMV:
- In the leaves – a mosaic appears, which is particularly noticeable on young leaves and at the growth vertices. In some cases, there is narrowing of the leaflet blade, and in certain cases the leaves become entirely threadlike (“shoestrings”).
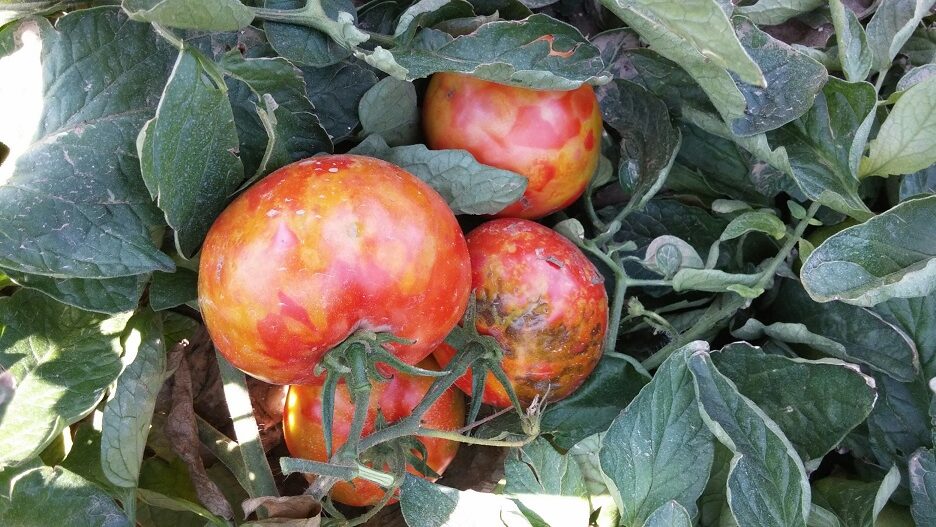
- In the fruit – yellow spots develop which become necrotic at a later stage. In some cases, “chocolate spots” appear on the fruit. In cases of severe damage, the fruit becomes wrinkled and distorted. The virus name (“Brown Rugose Fruit”) was given due to the wrinkled appearance together with the brown spots.
- Note that in contrast to the characteristic situation when affected by ToMV, in which symptoms generally appear in the fruit only in cases of particularly severe damage to the foliage, in the case of ToBRFV – there is no connection between the severity of damage to the fruit and severity of damage to the foliage: there are situations in which serious damage to the fruit is observed while no symptoms appear on the leaves, or vice versa – cases of severe symptoms in the foliage and lack of symptoms in the fruit.
- In certain cases – necrosis develops of the calyx of the fruit, the fruit peduncle, and the central spine of the cluster of fruit.
- When a susceptible variety is infected with ToBRFV, the main damage is a significant weakening of the plant and its capability to produce clusters of fruits over a long season.
In the wake of the viral infection, tomato cultivation in Israel has changed entirely: due to the weakening of the plants, growers currently have almost no possibility to grow tomatoes in a long central season of 9-10 months as was customary before the virus’s appearance; instead, shorter growing seasons of 4-5 months are now customary, intended for harvesting a few clusters only.

Symptoms on leaves – severe mosaic and narrowing of some of the leaf lobes, to the point of appearing “thready”

Severe symptoms in the fruits
Symptoms of necrosis in the calyx, fruit peduncle and the spine of the cluster
Weakening of the plant as a result of viral infection in a susceptible variety (on right) compared to a variety that is largely similar to it but is resistant to the virus (on left).
How is the disease transmitted?
- ToBRFV is very easily transmitted mechanically – by human contact, by work tools, support wires, or any entity that comes in physical contact with an infected plant or soil that contains the virus and later comes in contact with healthy plants. It is important to remember that particles of this virus are particularly resistant to environmental conditions, and are capable of surviving for long periods in soil or on infected surfaces.
- Since the virus is capable of surviving in soil for a long period – the virus is also transferred with infected soil that is moved from one place to another (by sticking to shoes, to work tools that are moved from one plot to another, etc.).
- The virus is transmitted in seeds – a seed produced from an infected plant is likely to carry virus particles on its surface.
- The virus can also be transmitted by bumble bees, which serve to pollinate during the cultivation process.
Prevention and treatment
- Since the outbreak of the disease, Hazera together with Limagrain Group have been working on a comprehensive study of the issue, in which tomato varieties with intermediate levels of resistance to the virus were developed. The first patent in the world for resistance to ToBRFV was registered by Limagrain in 2017. Using these varieties provides an optimal solution for growing tomatoes in conditions of infections with ToBRFV, while maintaining the varieties performance.
- Observing phytosanitary rules is key to preventing the disease:
- Making sure to have clean clothes, jackets and gloves for those entering the greenhouses.
- Making sure to sterilize all equipment used.
- Sterilizing shoes in an immersion pit upon entrance to the greenhouse.
- Being strict about the order in which buildings are entered – the workday begins with the buildings housing the young, healthy plants and continues to the buildings housing the more mature plants.
- Plants in which infection is discovered should be immediately removed from the greenhouse, being careful to avoid contact with neighboring plants.
- Using healthy seeds and seedlings is another key to preventing the disease. Hazera is strict about performing health tests in licensed laboratories, according to international standards and the Plant Protection Services. Checking that seeds are free of ToBRFV is done by the ISHI Protocol, which is the international protocol accepted throughout the world.
- Being strict about good sanitization – sterilizing the soil or growth medium and the greenhouse space when cultivation is completed.